What does a Heart Attack look like on an EKG?

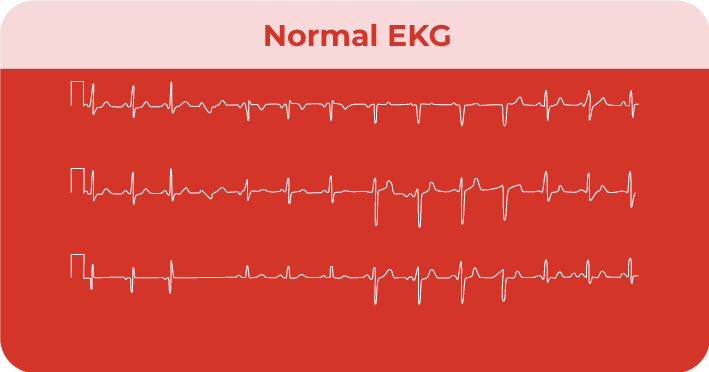
What is an EKG?
An EKG, or an electrocardiogram, is a quick and non-invasive way of providing important information about the heart. Specifically, EKG’s record the heart’s electrical signals and can detect arrhythmias or a previous heart attack.
Common symptoms that call for an EKG include:
- Chest Pain
- Heart Palpitations
- Rapid Pulse
What Causes a Heart Attack?
Heart attacks usually occur when cholesterol and fat build up in the arteries, creating blockages that can form blood clots and restrict blood flow to the heart.
Blocked blood flow leads to Ischemia, meaning parts of your body aren’t getting enough blood. If too much heart muscle sustains damage, the heart may not supply enough blood to the body.
What is a Silent Heart Attack?
A silent heart attack is a heart attack that has mild symptoms, or unnoticeable symptoms. Those who suffer a silent heart attack may think they just have had heartburn or the flu.
Some symptoms include: Mild chest pain, shortness of breath and flu-like symptoms.
Can an EKG detect a Heart Attack?
Yes, EKG’s have to potential to detect heart attacks. An ECG can reveal if you had a silent heart attack up to months or years ago.
However, EKG’s are not the most accurate in detecting prior silent heart attacks. Rather, they are best used when combined with other imaging tests like Blood Tests, CT Scans and Cardiac MRI’s.
Blood Test
Blood tests are commonly used to check for a heart attack by identifying the presence of the troponin. After a heart attack, troponin levels may be high for 1 to 2 weeks, which may help diagnose heart attacks.

CT Scan
A Computer Tomography (CT) Scan utilizes X-Rays to capture 3D images of the heart and the heart vessels. With a CT scan, your doctor will be able to clearly see and examine:
- Coronary Arteries
- Pulmonary Veins
- Heart Chambers
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac MRI’s, also referred to as heart MRI’s, create images of the heart and blood flow using radio waves and magnets. Aside from diagnosing a previous heart attack, medical providers may also order a Cardiac MRI to check for heart damages and areas where there is a lack of blood flow.
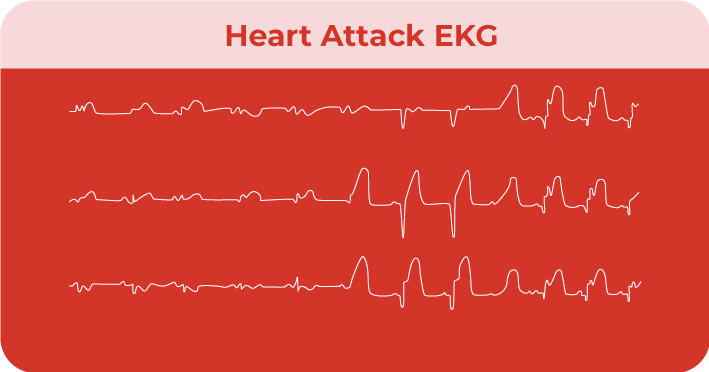
What does a Heart Attack Look Like on an EKG?
An STEMI heart attack will have an elevated ST segment with a T wave that is more peaked than normal.
On the other hand, an Non-STEMI heart attack will show up on an EKG in the following ways:
- Transient ST-elevation: ST Segment peaks for a short period(s)
- ST-Depression: ST-segment drops below the normal baseline
- T-wave Inversion: The T-Wave will curve downward